Summary
Top acrylic customization techniques: laser cutting, engraving, and thermoforming encompass a range of advanced methods used to modify acrylic materials for various applications. Acrylic, known for its optical clarity, strength, and versatility, serves as a popular alternative to glass in numerous industries, including signage, art, and product design. Notable techniques such as laser cutting and engraving allow for precision and creativity, enabling the production of intricate designs and cus- tomized products that meet the specific needs of clients and consumers alike.
Table of Contents
Laser cutting is a prominent technique that utilizes a focused laser beam to achieve high precision in cutting and engraving acrylic, often yielding cleaner edges and complex shapes. This method is particularly valued for its efficiency and minimal material waste, making it ideal for both large-scale production and bespoke projects. On the other hand, laser engraving adds aesthetic value by creating detailed markings on the acrylic surface, enhancing the appeal of personalized items and industrial components. Both methods are complemented by thermoforming, a process that shapes heated acrylic sheets over molds, allowing for the creation of three-dimensional designs that are widely used in packaging and automotive parts.
The versatility of these acrylic customization techniques has led to their widespread adoption across various sectors, with applications ranging from artistic creations to functional components in manufacturing. As the demand for personalized and sustainable products increases, advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in acrylic customization, fostering innovation while also presenting challenges in cost management and material sourcing. Overall, understanding the distinctions and applications of laser cutting, engraving, and thermoforming is crucial for leveraging the full potential of acrylic materials in modern design and production.

Overview of Acrylic Materials
Acrylic, commonly known by trade names such as Plexiglas® and Perspex®, is a versatile thermoplastic that is widely used as a shatter-resistant alternative to glass due to its optical clarity and strength. It can be categorized into two primary types: cast acrylic and extruded acrylic, each with distinct properties and applications.
Types of Acrylic
Cast Acrylic
Cast acrylic is produced by pouring liquid acrylic into molds and allowing it to cure. This manufacturing process yields acrylic with exceptional optical clarity and a consistent molecular structure, making it ideal for high-quality applications such as custom awards and trophies, signage, and decorative designs. Cast acrylic is particularly favored for laser engraving, as it turns a frosty white color when engraved, providing a striking contrast that enhances the visual appeal of the final product.
Extruded Acrylic
In contrast, extruded acrylic is manufactured through a process that pushes acrylic resin through rollers to form sheets. This continuous manufacturing technique makes extruded acrylic more cost-effective and results in uniform thickness, making it suitable for large-scale projects. While extruded acrylic is excellent for laser cutting due to its flame-polished edges, it is less suitable for engraving, as it produces a clear engraving rather than a frosted finish.
Properties of Acrylic
Acrylic exhibits numerous advantageous properties, including high impact resistance (up to ten times that of glass), excellent dimensional stability, and low water ab- sorption. It also demonstrates remarkable resistance to ultraviolet (UV) light and various chemicals, making it weatherable and ideal for outdoor applications. Available in a wide array of colors, finishes, and coatings (such as antimicrobial and scratch-resistant), acrylic can be customized to meet the specific needs of diverse projects.
Applications of Acrylic
The applications of acrylic are extensive, encompassing various sectors from mar- keting to art and design. Common uses include marketing signs, lenses, furniture, glass replacement, and artistic products. Its ability to be laser engraved or cut further enhances its versatility, allowing for intricate designs and functional products in both commercial and personal projects.
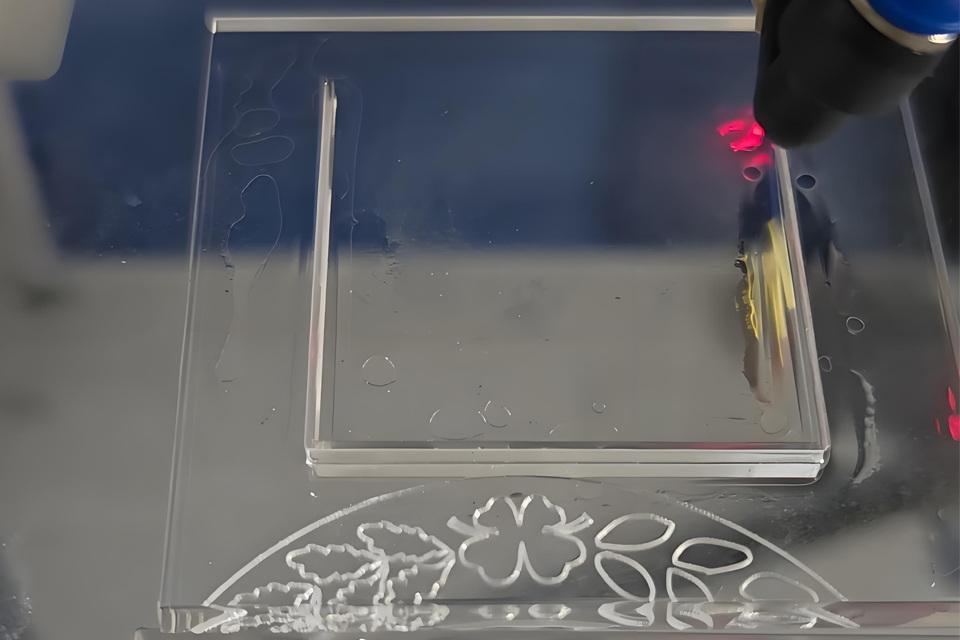
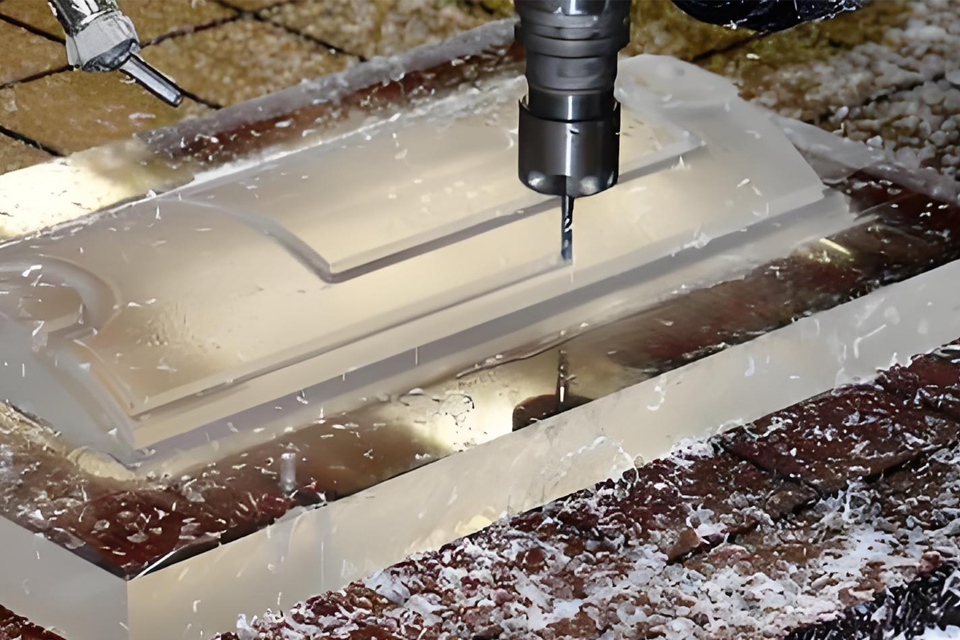
Laser Cutting Techniques
Laser cutting is a sophisticated technology that employs a high-powered laser beam to cut, engrave, or mark a variety of materials, including acrylic. This method involves focusing the laser onto the material’s surface, where it either melts, vaporizes, or oxidizes the material along a predetermined path, allowing for high precision and intricate designs.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting offers numerous benefits, including: High Precision: Laser cutters can achieve extremely fine cuts, often less than 0.1mm in diameter, making them ideal for intricate designs. Minimal Material Waste: The narrow kerf produced by laser cutting results in less waste, which is especially advantageous when working with costly materials. Versatility: Laser cutting can handle a wide range of materials, including dense woods, soft metals, and various plastics. Automation and Integration: The technology allows for the integration of smart fea- tures such as CAD/CAM software, enhancing precision and efficiency.
Principles of Laser Cutting
The fundamental principle behind laser cutting involves generating a concentrated beam of light, typically produced by a laser resonator. This beam is focused through a series of lenses and mirrors to create a small, intense spot that is directed onto the material. As the beam interacts with the material, it either melts, vaporizes, or ablates the material in its path, resulting in precise cuts. Computer numerical control (CNC) systems are employed to automate and control the movement of the laser, ensuring accurate and repeatable cutting operations.
Types of Lasers Used
Various types of lasers can be utilized for cutting acrylic, with carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers being the most common due to their effectiveness in cutting non-metallic materials. These lasers generate a high-energy density beam that allows for efficient cutting while minimizing heat-related distortions.
Applications of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is widely used across various industries, including automotive manu- facturing, aerospace, electronics, and the metal industry. It is particularly valued for its ability to cut complex geometries with precision and speed, making it a preferred choice for high-volume production runs.
Future Developments
Advancements in laser cutting technology are expected to enhance precision, effi- ciency, and versatility. Innovations such as higher wattage lasers, improved cooling mechanisms, and robotic automation will further streamline the cutting process and increase productivity while reducing the need for human intervention.
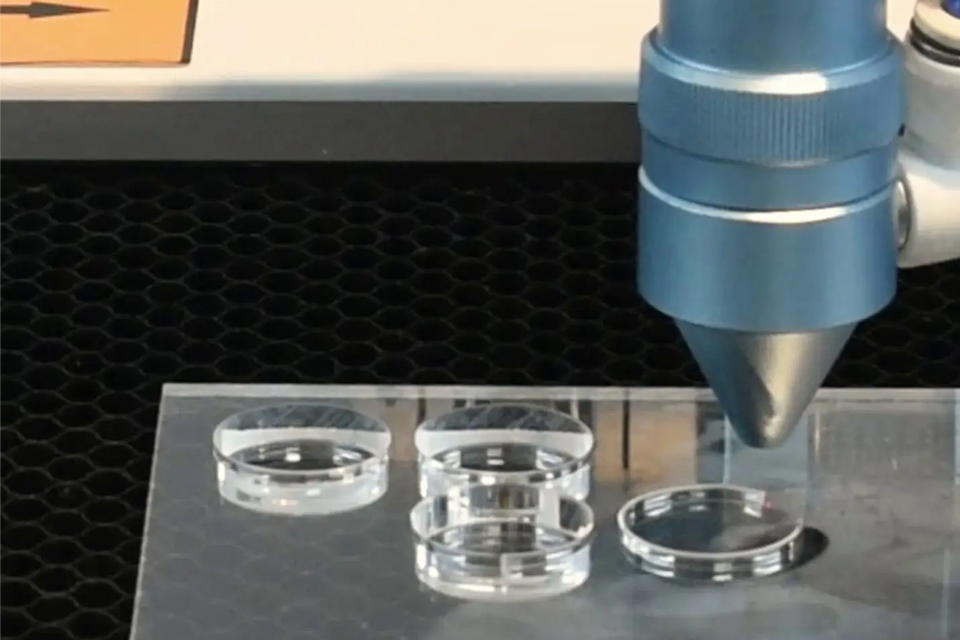

Engraving Techniques
Laser engraving is a precise method that employs a focused laser beam to etch de- signs, text, or artwork onto various materials, particularly acrylic. This technique is widely favored due to its ability to produce intricate details and a variety of visual effects, making it a popular choice in industries ranging from art to manufacturing.
Laser Engraving Process
The laser engraving process involves the use of a high-energy laser beam to create fine markings by either oxidizing, scorching, or vaporizing the surface of the mater- ial. The power settings of the laser are crucial; lower power is typically employed for engraving, which helps to avoid excessive melting and ensures clarity in the final design. Additionally, the engraving should be conducted prior to cutting the acrylic to prevent any melted edges that could compromise the quality of the finish.
Types of Acrylic Suitable for Engraving
Two primary types of acrylic are commonly used in laser engraving: cast and extruded acrylic. Cast acrylic is preferred for engraving due to its ability to produce a frosted, contrasting finish that enhances visibility of the design. In contrast, extruded acrylic, while suitable for cutting, tends to yield a smoother, more transparent result that may diminish the distinctiveness of the engraving. Each type has its unique advantages depending on the desired outcome and application.
Advantages of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving offers numerous benefits, including high precision and flexibility in design. Adjusting laser parameters allows for various engraving depths and effects, catering to different artistic and functional requirements. Furthermore, it is a non-contact method, which means it does not physically alter the surface of the material being engraved, thereby preserving its integrity.
Applications of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving finds application across multiple sectors. It is extensively used in creating custom gifts, small-scale decor items, and personalized gadgets. The ability to personalize products, such as engraved photo frames and customized phone cases, has significantly increased its popularity in the consumer market. Moreover, the technique is also employed in industrial settings for marking and etching components, enhancing branding and product identification.
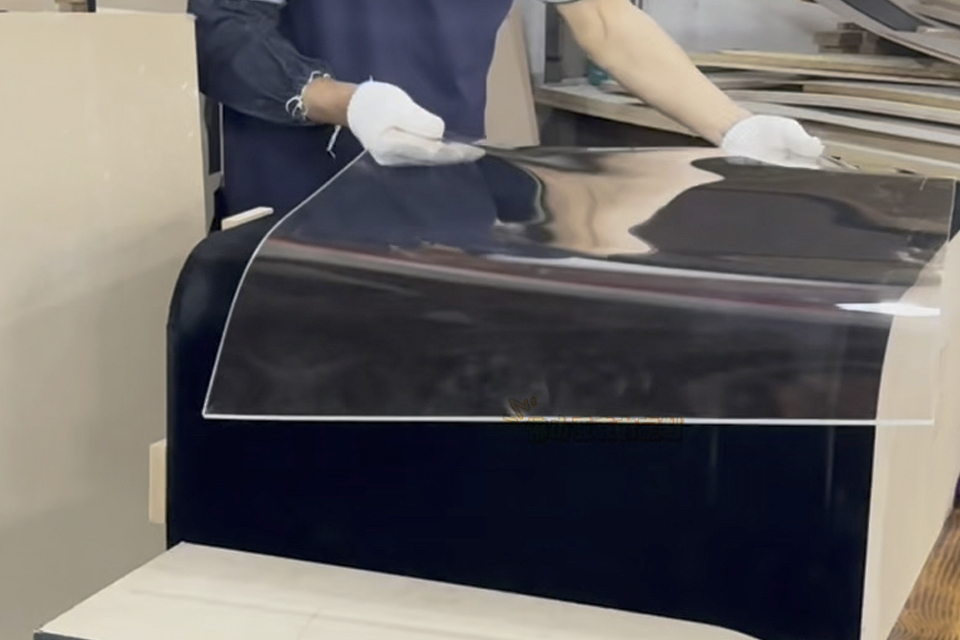

Thermoforming Techniques
Thermoforming is a versatile plastic manufacturing process that involves heating thermoplastic sheets until they become pliable and then shaping them over molds to create specific three-dimensional designs. This technique is widely used for producing a variety of plastic products, including containers, lids, and automotive components. The efficiency and cost-effectiveness of thermoforming make it a preferred choice for many manufacturers compared to other molding methods.
Common Thermoforming Processes
Several key processes fall under the umbrella of thermoforming, each offering unique advantages depending on the desired outcome and product specifications.
Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming is one of the simplest and most widely used thermoforming tech- niques. In this process, a heated plastic sheet is draped over a mold, and a vacuum is applied beneath the sheet, pulling it tightly against the mold surface. This method is particularly valued for its cost-effectiveness and speed, making it suitable for producing items like packaging and display cases. However, controlling the distribution of thickness can be a challenge, as the part’s edges may be thicker than its center.
Pressure Forming
Pressure forming is a variation of vacuum forming that enhances the detail and definition of the final product. In this method, air pressure is applied in addition to the vacuum, which forces the heated plastic sheet against the mold with greater intensity. This extra pressure enables the creation of intricate designs, including textures and sharp edges, which are more difficult to achieve with vacuum forming alone. Pressure forming typically involves using pressures up to 200 psi to ensure high-quality details in the final products.
Mechanical Forming
Mechanical forming employs direct mechanical force to shape the plastic sheet. In this process, a core plug is used to push the pliable sheet into the mold, imprinting intricate surface patterns onto the material. This technique is particularly advan- tageous when precision and high levels of detail are required, making it suitable for specialized applications such as medical device components and high-end consumer products.
Acrylic Tips
Select the right acrylic type and thickness, confirm digital proofs, choose polished or frosted edges, specify UV printing or LED integration, add precise drilling and mounting, and pack securely for safe delivery.
Matched Mold Forming
Matched mold forming is a sophisticated thermoforming method where two matched molds are used to shape the heated sheet. This technique allows for complex geometries and provides a high-quality finish on the final product. It is particularly effective for producing items that require both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity, such as automotive parts and custom-designed containers.
Benefits of Thermoforming
The thermoforming process is characterized by its rapid cycle times, cost efficiency, and the ability to produce both small and large production runs effectively. It al- lows for a wide range of design creativity, making it suitable for various industries, including packaging, automotive, and consumer goods. Furthermore, the light- weight nature of thermoformed products compared to metal alternatives can result in significant cost savings in transportation and assembly, further enhancing their attractiveness for manufacturers.
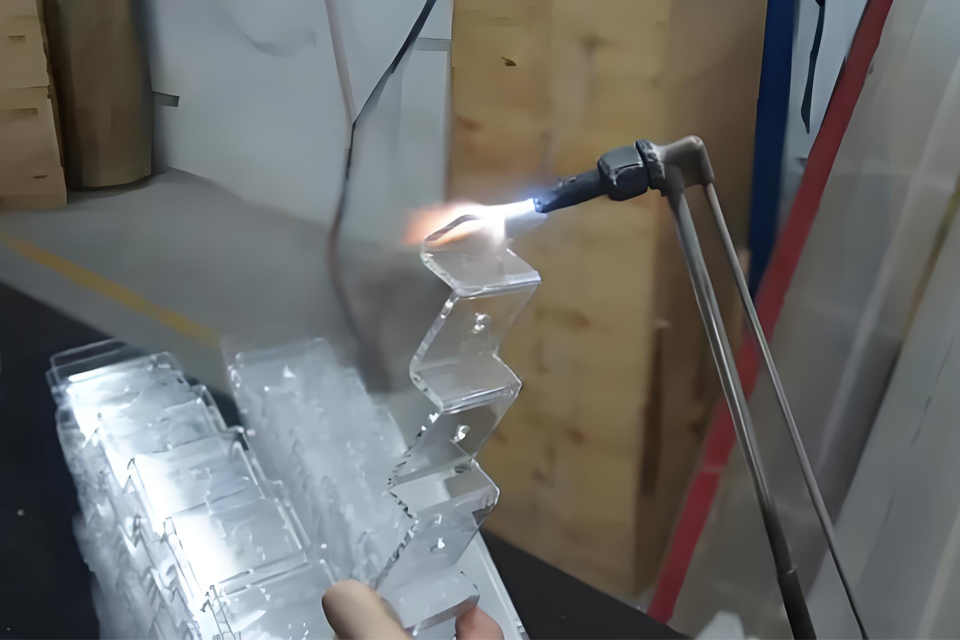

Comparison of Techniques
In the realm of acrylic customization, two prominent techniques, CNC routing and laser cutting, each offer distinct advantages suited to different project requirements. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the most appropriate method for a specific application.
CNC Routing
CNC routing is particularly beneficial for larger pieces of acrylic or when dealing with less intricate designs. This technique utilizes a rotating cutting tool to carve out shapes and patterns, allowing for the effective machining of thick materials. It is often favored for its ability to handle substantial volumes of material, making it suitable for mass production. Additionally, CNC routers provide a broader range of tool options, which can create various textures and finishes on the acrylic surface.
Advantages of CNC Routing
Versatility with Material Thickness: CNC routers excel in working with thicker acrylic sheets, offering the ability to cut, shape, and engrave with precision. Cost-Effectiveness for Large Projects: When producing larger quantities, CNC routing may offer a more economical solution, as it generally has lower operational costs for high-volume production.
Laser Cutting
On the other hand, laser cutting is recognized for its precision and the ability to create intricate designs with fine details. This technique employs a focused laser beam to cut through the acrylic, providing cleaner edges and the possibility for more complex shapes that CNC routers may struggle to achieve. Laser cutting is particularly advantageous for detailed engravings and designs that require a high degree of accuracy.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
Precision and Detail: Laser cutting delivers exceptional detail, making it ideal for projects that require intricate patterns or fine text. Minimal Heat Affected Zone: The process generates less heat compared to CNC routing, resulting in cleaner cuts and reduced risk of material warping or melting.
Quick Setup and Operation: Laser cutters can often be programmed quickly for new designs, facilitating faster turnaround times for custom projects.
Choosing Between Techniques
When deciding between CNC routing and laser cutting, several factors should be considered, including the complexity of the design, material thickness, production volume, and cost considerations. For larger, less detailed projects or high-volume production runs, CNC routing may be the preferred choice. Conversely, for intricate designs and smaller production needs, laser cutting may provide the superior option due to its precision and efficiency. Ultimately, the choice between CNC routing and laser cutting hinges on the specific demands of the project at hand, balancing factors such as cost, time, and design intricacy to achieve the best outcome.
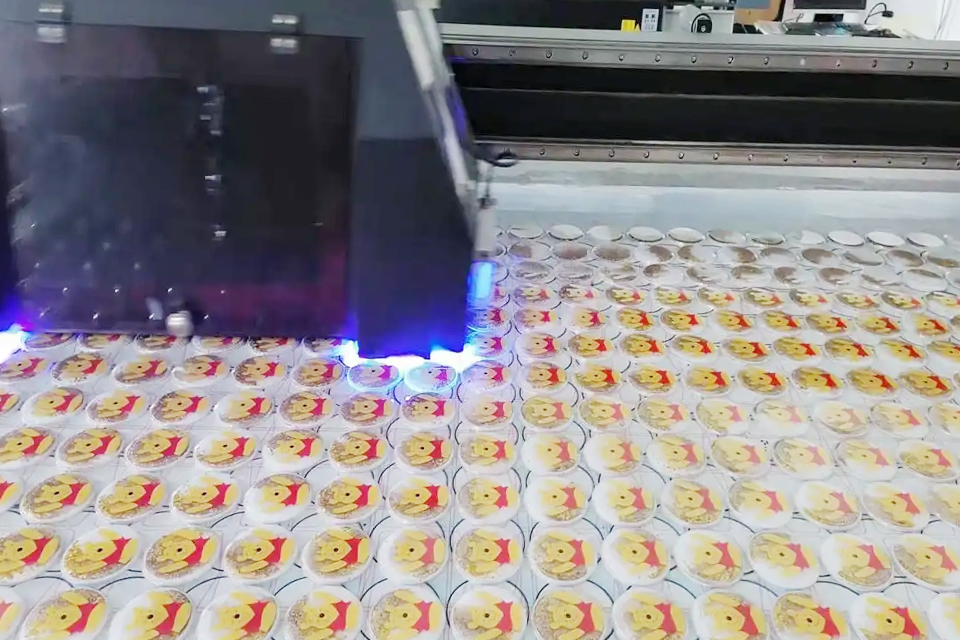

Innovations and Trends
Recent Advancements in Acrylic Customization
The acrylic industry has witnessed significant innovations in recent years, primarily driven by the demand for customization and sustainability. Innovations such as precision casting and advanced extrusion techniques have notably improved the surface quality and consistency of thick acrylic sheets, enhancing their appeal and performance in various applications. The push towards eco-friendly materials has also spurred the development of sustainable practices, leading to new market opportunities within the sector.
Thermoforming in Acrylic Production
Thermoforming has emerged as a key method in acrylic customization, allowing for the efficient production of complex shapes and designs. This process involves heating an acrylic sheet until pliable, then forming it over a mold through methods like vacuum or pressure forming. The advantages of thermoforming include cost efficiency, as it enables manufacturers to produce large components quickly and affordably compared to other methods, making it particularly attractive for industries such as automotive and consumer goods. Moreover, the versatility of thermo- plastics used in thermoforming contributes to the rapid growth of acrylic applications across different sectors.
The Role of Laser Technology
Laser cutting and engraving technologies are integral to the customization of acrylic products. Laser cutting allows for precise cuts with minimal material distortion, while laser engraving offers detailed markings on the surface of acrylic materials. These techniques have expanded the potential for creating intricate designs and personalized items, catering to specific client needs without the lengthy lead times associated with traditional manufacturing methods. The market for acrylic 3D printing, which complements these technologies, is projected to grow significantly, indicating a robust trend towards innovation in acrylic customization.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite these advancements, the acrylic customization industry faces challenges, particularly in managing costs while investing in new technologies and materials. The rapid pace of technological change requires manufacturers to remain compet- itive, prompting them to adopt more efficient and automated processes. However, these challenges also present opportunities; the increasing demand for customized and personalized products allows manufacturers to diversify their offerings and cater to niche markets. Overall, the ability to adapt to these evolving trends will be crucial for the ongoing success and innovation within the acrylic customization industry.